Understanding Computer Components Guide
Author: Luke Adkins Date Posted: 19 September 2023
Are you overwhelmed by the multitude of computer terms and jargon? At Australian Computer Traders, we're here to simplify the world of computer components for you. We break down the 'techno-speak' to make your experience smoother when shopping for a refurbished computer. In the following sections, we'll delve into every major computer component you should be familiar with, translating the complex terminology into practical insights to help you make informed decisions.
If you have any more questions, please give call our dedicated support team on 1300 727 516 or send us an enquiry.

Computer Processor (CPU)
The processor (CPU) is the brain of the computer. This is what runs your software, calculations, and operations. A processor is made up of multiple cores – think of these as additional brains working together to perform several tasks at once.
There are different types, and generations of processors. Some have different clock speeds, and cache, so it's not always as simple as 'choosing the processor with the highest numbers'.
Intel Processor Comparison
| Processor Series | Number of Cores | Hyper-Threading | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intel Core i3 | 2-4 | Yes (10th gen+) | Basic tasks |
| Intel Core i5 | 4-6 | Yes (9th gen+) | Moderate computing |
| Intel Core i7 | 4-8 | Yes | High-performance tasks |
| Intel Core i9 | 8-24 | Yes | Professional and intense computing |
| Intel Xeon | 4-56 | Yes | Server, Workstation, Datacenter |
Branding Series
- ‘H’ series = High-performance.
- ‘P’ series = Performance optimised.
- ‘T’ series = Power-optimised.
- ‘U’ series = Mobile power efficient.
- ‘Y’ series = Extremely low power usage.
The Intel Core series of processors are refreshed every year. As a rough guide, there is approximately a 10-15% difference in performance between generations.
Motherboard
A motherboard (or logic board) is the main circuit board of your computer, connecting all the essential components such as the CPU, RAM, storage devices, and peripherals. It acts as the communication hub, allowing these parts to work together seamlessly.
Think of it as the backbone of your PC, providing power, data transfer, and connectivity for all the parts that make your computer function. Without a motherboard, your computer wouldn't be able to run.
Motherboards come in various sizes, catering to different needs and form factors. When it comes to laptops, there are no 'standard' sizes for motherboards. These are usually custom-made to suit the type of laptop, and feature a soldered CPU, and sometimes RAM and Storage Devices. As there is no standard for laptop motherboards, you generally cannot simply buy a replacement motherboard if the board in your laptop was to fail. Desktop computers on the other hand are a different story, as there are a few standard types of motherboards available. The size of the board depends on your case compatibility and the features you require for your computer build.
Motherboard Types:
- ATX: The standard-sized motherboard, ATX, offers ample space for components and expansion slots. It's a popular choice for gamers and power users.
- MicroATX: A slightly smaller motherboard, microATX, provides a balanced mix of features and compactness. It's a good choice for smaller cases and budget-friendly builds.
- Mini-ITX: Mini-ITX motherboards are the smallest and most compact, making them perfect for compact and portable systems. However, they may offer fewer expansion options compared to larger sizes.
It's worth noting that brands such as Dell, HP & Lenovo use proprietary motherboards, and other components inside some of their desktop computers.
Computer Memory. What is RAM?
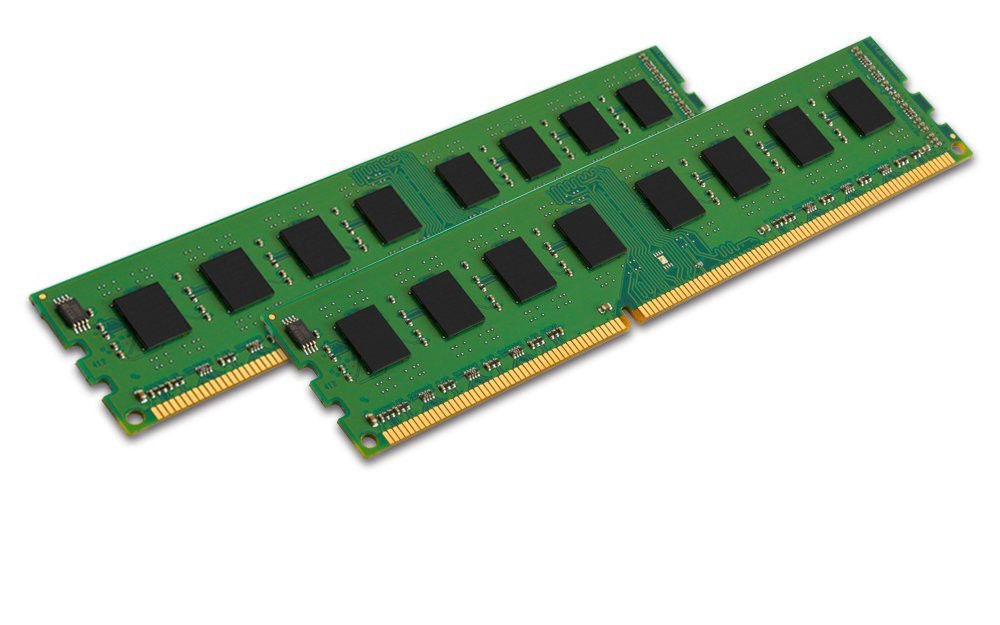 RAM stands for Random Access Memory.
RAM stands for Random Access Memory.- RAM is able to store a small amount of data, but with extremely high speeds.
- RAM is volatile, meaning it loses all the data stored in it when the power goes off.
Installing more RAM into your computer does not always improve performance, unless the program you're using actually needs more. Currently, to use more than 8 GB of RAM, you have to have quite a few programs running, several web browser tabs open at the same time, or play intensive games.
- 8 GB of RAM is considered the standard these days for general day-to-day use, and is recommended to run Windows smoothly.
- 16 GB of RAM can be useful for users operating with a fair amount of data and larger workloads.
- 32 GB of RAM (or more) is great for servers, intensive graphics design, and data centre applications.
Applications where larger amounts of RAM could be beneficial include: having many web browser tabs open at once, streaming video or audio, gaming, video editing, audio engineering, and running multiple Virtual Machines. For example, the popular web browser Google Chrome is known to be a 'resource hog', as having many browser tabs open at one time can fill your system's RAM quite quickly.
Solid State Drives vs Hard Drives
A hard disk drive (HDD) is one of two types of drives available for storing your data, along with solid-state drives (SSD).
Both options can be used to install your operating system and applications, as well as any data files, such as videos, audio,
documents and photos.
- HDD’s are slower than SSD’s, but can offer great value for money as you get larger amounts of storage at cheaper prices.
- SSD’s have no moving parts and as such are faster and less prone to failure than HDD’s.
- A 256 – 500 GB Solid-State Drive is recommended for the average user.
For the best of both worlds, we recommend installing an SSD for your main boot drive.
This is where your operating system is installed (such as Microsoft Windows).
We recommend using a SSD to store your commonly used day-to-day programs, as well as any files you frequently access
or are of a more demanding nature.
You can use a HDD as a secondary storage drive for photos, videos, files and less intensive programs.
Graphics Card (GPU)
.png) The Graphics Card (also known as a ‘video card’) is a piece of hardware containing the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU), which builds pictures and then displays them on your screen.
The Graphics Card (also known as a ‘video card’) is a piece of hardware containing the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU), which builds pictures and then displays them on your screen.
Your resolution typically has the greatest impact on your GPU's performance.
1920x1080, also known as 1080p, is the standard resolution for modern gaming, but mid-tier/low-tier GPU’s may play modern games more easily at reduced resolutions.
- The Nvidia GT1030 (2 GB) is an entry-level video card for current games. This GPU should be able to play some modern games at low to medium settings.
- The Nvidia GTX1650Ti (4 GB) is considered a current-generation gaming level video card. This GPU should play most modern games with ease at 1080p resolution.
For those users who require multiple monitors, having a dedicated Graphics Card installed into your PC can enable support for up to 4 monitors to be connected at one time.
Power Supply Unit (PSU)
Power Supply Units are the unsung heroes of your computer system. They play a pivotal role in ensuring your PC runs smoothly and reliably. At its core, a PSU is responsible for converting the electricity from your wall outlet into a stable and consistent form of power that your computer's components can use. It provides the necessary voltages and currents to keep everything from your CPU to your graphics card running without a hitch. While desktop computers have their power supply installed inside the case, laptops have an external power supply (commonly known as an AC adapter) that supplies power to the laptop, and charges the internal battery.
Types of Desktop Computer Power Supply Units
- ATX Power Supplies: These are the standard power supplies used in most desktop computers. They are different wattage power supplies available to accommodate varying levels of performance.
- Modular Power Supplies: Modular PSUs allow you to connect only the cables you need, reducing clutter and improving airflow in your PC case. They're a favourite among cable management enthusiasts.
- SFX Power Supplies: Small Form Factor (SFX) PSUs are designed for compact PC cases. They are smaller and more space-efficient while still delivering ample power.
It's worth noting that brands such as Dell, HP & Lenovo use proprietary power supplies, and other components inside some of their desktop computers.
We hope you now feel more confident and informed about making your next computer purchase - whether you're upgrading your CPU for gaming, choosing the perfect motherboard for your build, or deciding between an SSD and HDD for storage.
If you find yourself with any questions or uncertainty after reading this guide, please don't hesitate to reach out to our dedicated support team at 1300 727 516 or contact us via email.
We're here to assist you on your journey to finding the perfect computer components for your needs.